MO Fauvarque, BIG & W. Weissenhorn, IBS, Exploring ESCRT-III/UBPY interaction in endocytosis and autophagy
Background:
The linkage of ubiquitin monomers or polymers is a reversible post-translational modification regulating protein activity, endocytosis, or degradation by either the proteasome or the autophagy pathway. We are interested in deciphering the role of ubiquitin specific proteases (USPs) in the regulation of host responses -such as immune signaling and autophagy activation- to pathogens. We also develop drug screening strategies for modifying their activity in human cells. We previously selected UBPY (syn. UUSP8) as a crucial actor of autophagy from a systematic RNA interference screen in Drosophila fruit flies.
Objectives:
The present project aims at (1) deciphering UBPY function in immune receptor endocytosis and autophagy regulation using both cell biology and Drosophila genetics approaches, (2) describing the mechanisms and function of UBPY and ESCRT-III proteins interaction at the structural and cellular levels, (3) searching for chemicals inhibiting UBPY activity.
Team:
The project involves members of Fauvarque’s group : Dr. C. Barette (Drug screening); Dr. E. Soleilhac (HCS/HCA, autophagy monitoring), Dr. E. Taillebourg (Drosophila), Mme M. Mortier (Enzymatic assay) and X. Crespo (PhD, cell biology) and of Pr. W. Weissenhorn’s group (Structural studies, UVHCI) with a common recruitment of Dr. C Aguilar as a GRAL post-doctoral position (Structural analysis, drug screening). The project requires access to several GRAL platforms (PSB, Electron microscopy, CMBA).
GRAL recruitment:
One two-year Post-doctoral fellow and accompanying bench fees supported by this grant from January 2015.
Achievements (January-November 2015)
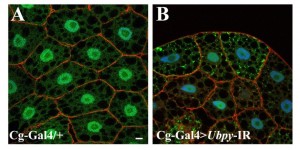
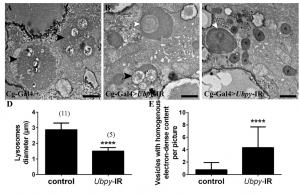
- We have completed an in vivo DUB screening and performed a deep analysis of UBPY function in intracellular trafficking using molecular genetics and transgenesis approaches in Drosophila. The corresponding results are described in a research manuscript entitled “The deubiquitinating enzyme UBPY is required for lysosomal biogenesis and productive autophagy in Drosophila” (Jacomin et al., 2015). In this paper, we show that Ubpy loss -of function results in the accumulation of autophagosomes due to a blockade of the autophagy flux. Furthermore, analysis by electron and confocal microscopy of Ubpy-depleted fat body cells revealed altered lysosomal morphology, indicating that Ubpy inactivation affects lysosomal maintenance and/or biogenesis. Lastly, we have shown the effect of shRNA mediated inactivation of UBPY in human HeLa cells in the deregulation of autophagy.
- We showed the interaction of UBPY with endocytic ESCRT-III protein in human cells and are currently investigating its function in cellular trafficking.
- An automated in vitro enzymatic assays has been set up in order to start a screening campaign for UBPY inhibitors.
Selected Publications:
- Jacomin et al., Plos One, 2015
- Weissenhorn and Fauvarque, Structure 2014 (comment)
- Effantin G et al., Cell microbiology 2013
- Taillebourg et al., Autophagy 2012
- Thevenon et al., Cell host microbe 2009
- Solomons J et al., Structure 2009
Figure 1. Silencing UbpY blocks the autophagic flux in Drosophila fat body.
Representative confocal sections of the larval fat body expressing a GFP-LC3B reporter gene. Actin is labelled with Phalloidin-Texas Red (red) and nuclei are labelled with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar: 10µm. Genotypes: (A) Cg-Gal4/+; UAS-GFP-LC3B/+, (B) Cg-Gal4/+; UAS-GFP-LC3B/ UAS-Ubpy-IR
Figure 2. Ultrastructural analysis of Ubpy silenced cells.
Control fat body cells (A) contain large autolysosomes (black arrowhead). These vesicles are characterized by their heterogeneous content and organelle remnants. In contrast, Ubpy silenced cells (B-C) contain autophagosomes whith non-degraded organelles (white arrowhead) (mitochondria in B and endoplasmic reticulum in C), small autolysosomes (black arrowhead) and vesicles with homogenous electron-dense content (asterisks). Scale bars: 1µm. Genotypes: (A) Cg-Ggal4/+, (B-C) Cg-Gal4/+; UAS-Ubpy-IR/+